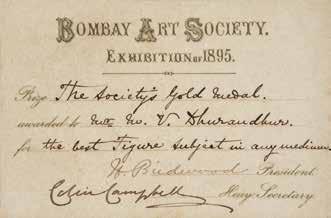1867

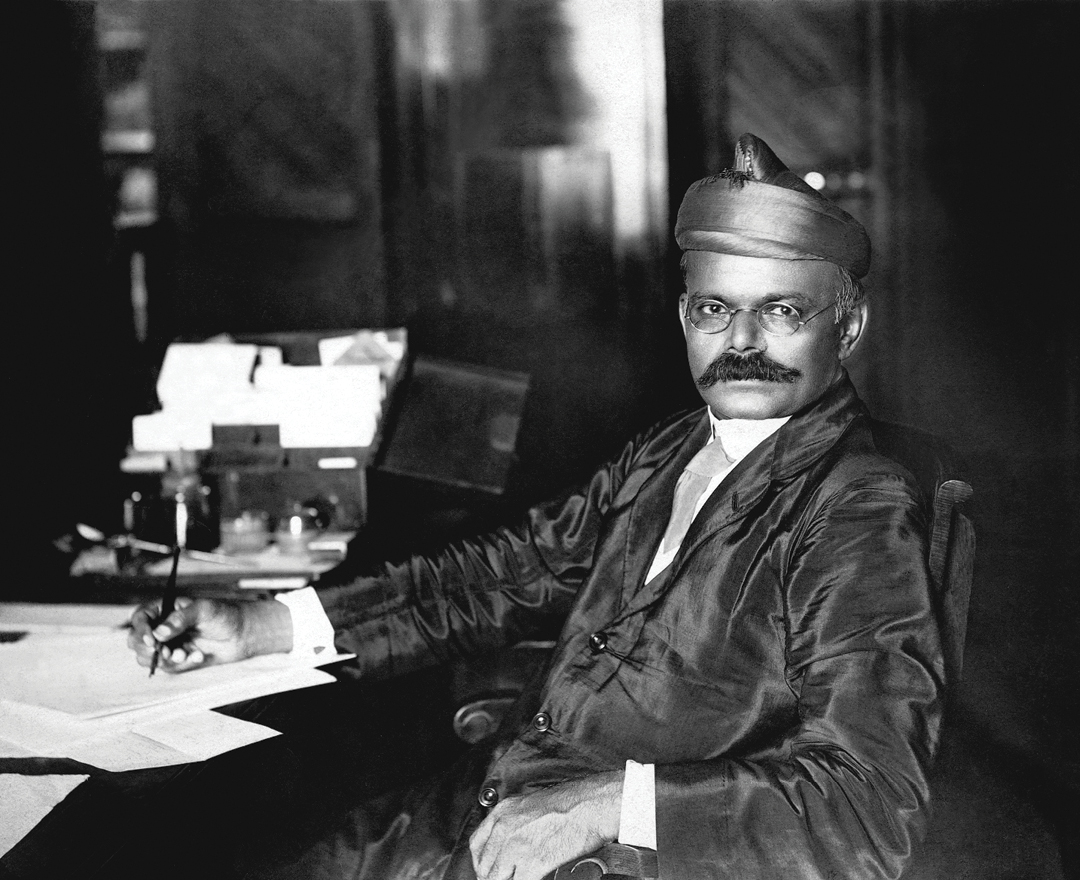
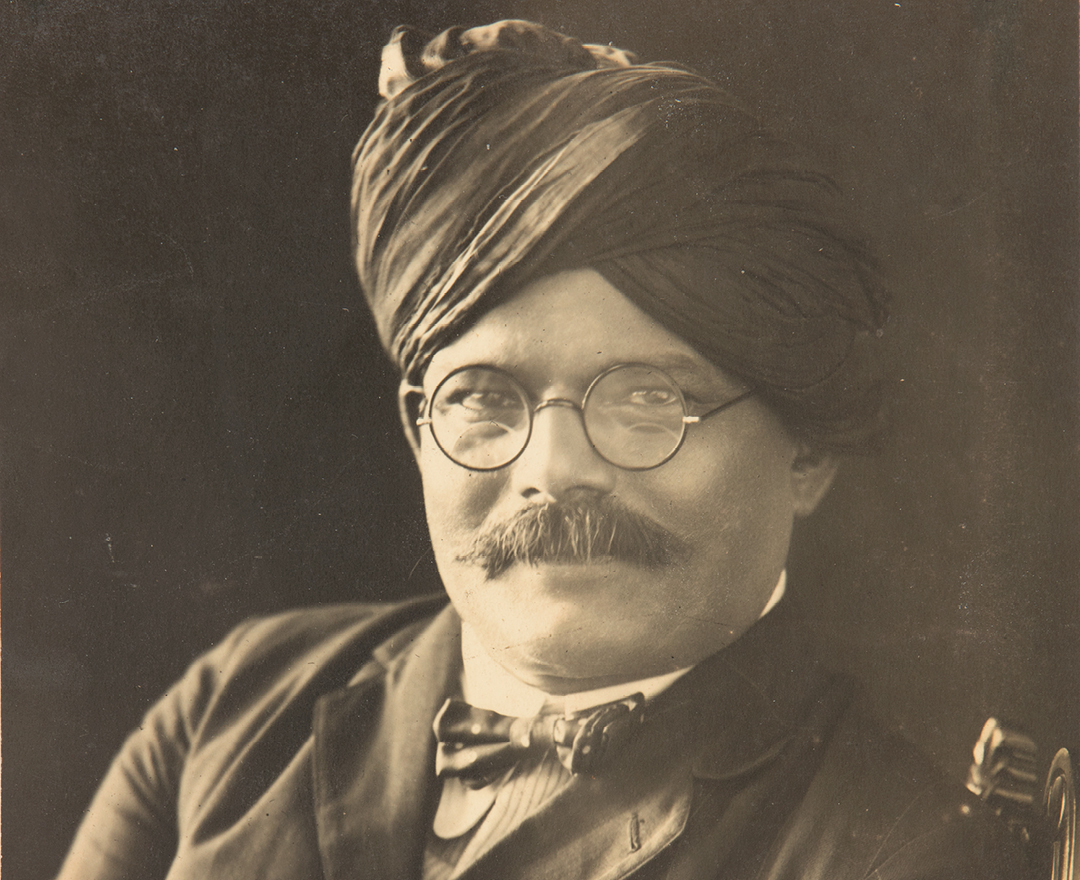
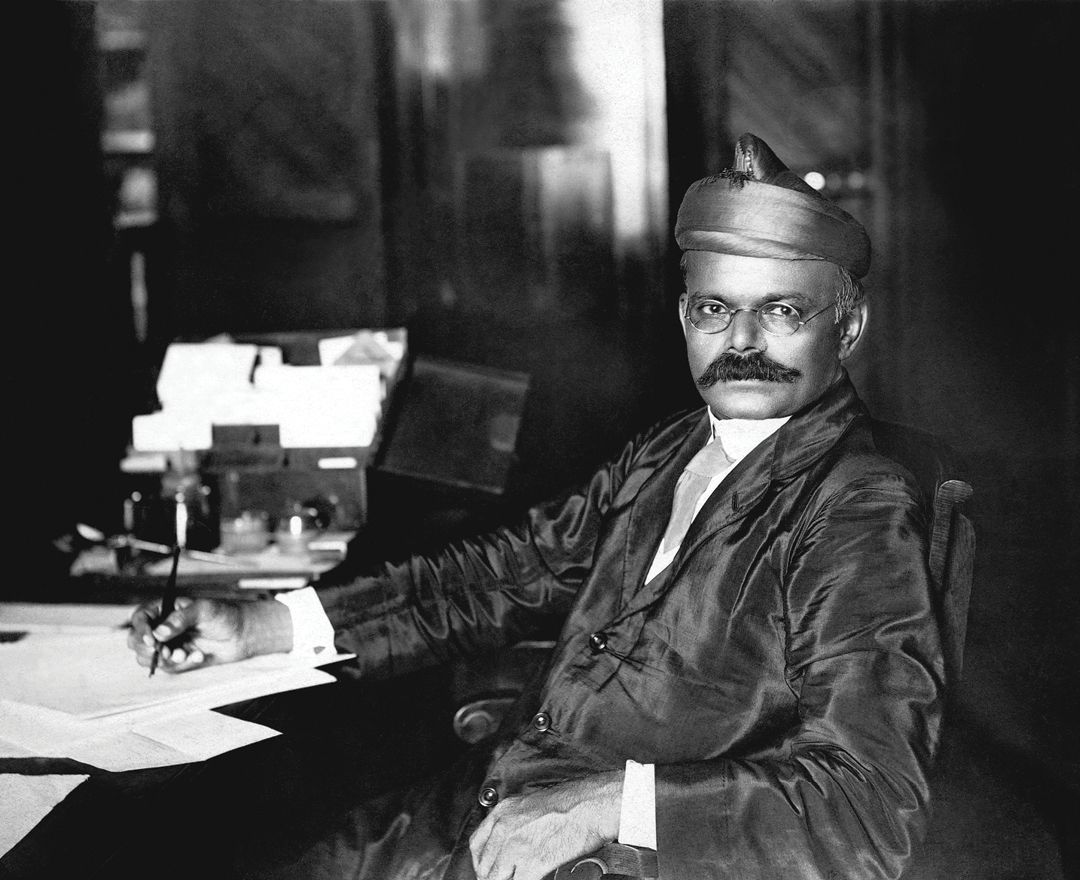
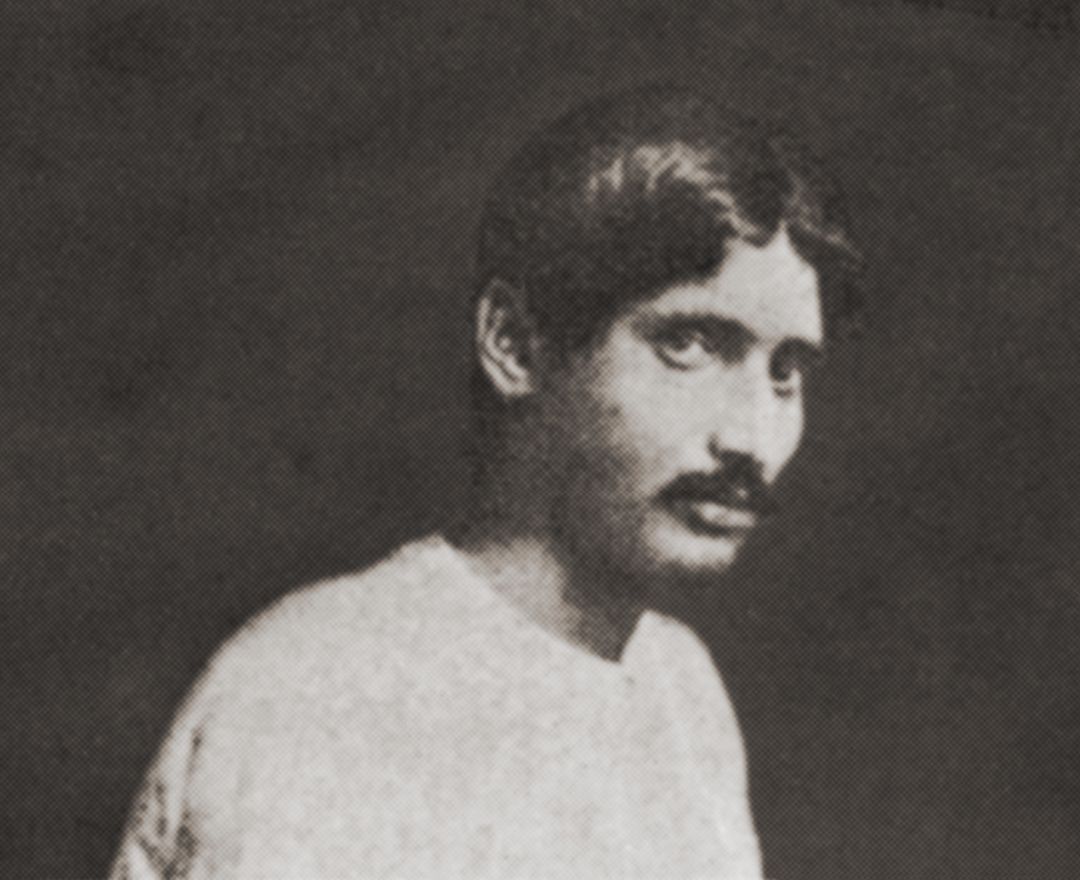
Mahadeo Vishwanath Dhurandhar is born on March 18 in a Prabhu
Pathare family of Bombay; spends his childhood in the princely state
of Kolhapur where his father is head clerk in the Political Agent’s
office; his early schooling is at Rajaram High School in Kolhapur
where his senior is Abalall Rahiman, his older brother’s friend, who
later joins Sir J. J. School of Art in Bombay and wins a gold medal at
an industrial exhibition sponsored by the British in Pune.
1891
Wins the school’s Waddington Prize for certificate design open only
to senior students; he is allowed to enter the competition on the
strength of his proposal that the teachers find exceptional.
Soon thereafter, his parents die in quick succession; starts teaching
art at Alexandra Girls’ High School to support his studies; secures
this job with the help of his teacher and vice-principal of Sir J. J.
School of Art, E. Greenwood; the latter also secures a scholarship to
help Dhurandhar financially.
1892

Still a student of Sir J. J. School of Art, obtains permission from
the school vice principal E. Greenwood and debuts at the Bombay
Art Society’s annual exhibition; wins an award for his charcoal
painting, Household Work; becomes the first Indian to receive an
award of the Bombay Art Society.
1894
Wins the Mayo Medal for being the most capable student in the
painting class; wins several other medals and awards during his
student days at Sir J. J. School.
Completes his graduation.
Travels to Ajanta caves as part of a project of the principal of Sir J.
J. School, John Griffiths.
Gets married to Bapubai in Kolhapur.
1895

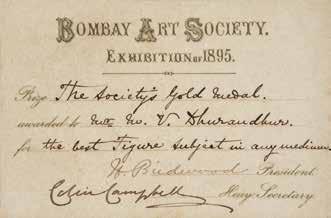
Paints Do You Come Laxmi? using oil on canvas for which he wins
the Bombay Art Society’s gold medal.
1896
Joins the faculty of Sir J. J. School on a short-term assignment
to teach; however, he spends the rest of his career at the school, gradually rising up the ladder to become its head in 1930.
His career as an artist grows steadily, and he goes on to become the
most popular academic Indian artist after Raja Ravi Varma.
His style is a commingling of the academic realism favoured by the
British colonials and Indian subjects drawn from history, mythology
and contemporary society.
Gets to meet his early inspiration Raja Ravi Varma at the eighth
exhibition of the Bombay Art Society, where one of his paintings,
The Music Lesson, impresses the stalwart; Varma buys the painting
and Dhurandhar goes on to make many works for the Raja Ravi
Varma Press.
1898

The plague epidemic in Bombay claims his wife, who leaves behind
an infant son, Ganapati; Dhurandhar’s painting of his wife, She is
Dead, becomes the first known instance of a mourning or deathbed
portrait by an artist of the Bombay School.
1899

Marries Gangubai in June.
Makes full use of opportunities available for a painter like him by
making commissioned illustrations for books, periodicals such as
Gujarati magazines Amar and Bhoot, calendars, advertisements,
postcards and so on.
1890s


Becomes especially popular for his postcards at a time of postcard
explosion in the West. Ethnographic postcards are chiefly used by
the British to write home and succeed the earlier ethnographic
paintings. His postcard painting Ayah is widely pirated.
Phenomenon of outdoor painting takes root in western part of
India and outflow of this kind of work becomes prodigious from the
late nineteenth century; Dhurandhar is one of the leading artists
of the genre besides Abalall Rahiman, N. R. Sardesai and S. L.
Haldankar.
1901


Art patron, author and publisher Sheth Purushottam Vishram
Mavji assigns Dhurandhar to make illustrations for his periodical
Suvarnamala this work goes on till 1913 during which time
Dhurandhar makes illustrations for numerous books and
magazines.
Sir J. J. School principal Cecil Burns tasks Dhurandhar and other
students to paint the scene on the river Shannon, commissioned by
the British government.
1905


Sheth Purushottam Mavji commissions Dhurandhar to paint the
history of Maratha ruler Shivaji; he also commissions the artist to
make paintings of his trip to Vaishnodevi in Jammu.
Cecil Burns appoints Dhurandhar and students to paint a bird’s eye
view of Alexandra Docks, commissioned by the British
government.
1907
Wins gold medal for his painting Naivedyam, at the Pandharpur
industrial exhibition; it is purchased by Bombay industrialist
Narottam Morarji.
1908
Paints a watercolour work featuring a number of figures, titled
Hindu Marriage Ceremony.
1910


Appointed head master of the painting department at Sir J. J. School
of Art.
His painting, Bride’s Maids wins gold medal at the industrial
exhibition in Jalgaon.
1911



Delhi is announced the new capital of British India; Dhurandhar
leads the J. J. team to Delhi to study the buildings to be painted,
he is subsequently assigned the painting of the Law Members’
Chambers; executes four panels of the size 4 ft x 24 ft comprising
two panels on the Hindu Civil Code, one on Sharia and another one
on the Last Will and Testament.
1912

Provides illustrations for By-Ways of Bombay by S. M. Edwardes.
Daughter Ambika is born on January 4; she goes on to become the
first female graduate of Sir J. J. School of Art in the 1930s.
Wins fifth gold medal for his painting Homage to their King at the
Gwalior fair; this watercolour is an elaborate court scene depicting
King George V and Queen Mary in India for the Delhi Durbar of
1911.
1914
Makes illustrations for Deccan Nursery Tales or Fairy Tales from the
South, a book by C. A. Kincaid, published in London.
1918
Becomes inspector of drawing at Sir J. J. School of Art, the first Indian to be
appointed to the post.
1920
Makes illustrations for the book Women of India by Otto Rothfield, published in Bombay by D. B. Taraporewala.
1920s
Gladstone Solomon introduces regular drawings from undraped
figures into the Bombay Art School’s curriculum. It is at this time
that the artist, who is already passionate about figure paintings, tries
to understand the nude figure through photographs and prints.
1921
Illustrates the book Tales of King Vikramaditya by Humphrey
1942
Milford, Oxford University Press; also illustrates an undated
publication, Meghdoot by Kalidasa, published by Purushottam
Vishram Mavji.
1926
Is commissioned by the ruler of the Aundh state (in present-day
Maharashtra), Bhawanrao Pantpratinidhi, to make paintings on
the life of Maratha ruler Shivaji.
1927
Awarded the title of Rao Bahadur by the British colonial government,
becoming the first Indian painter to be thus honoured.
1930
Becomes the first Indian director of Sir J. J. School of Art; appointed
to officiate for six months from May to October in the absence of
the school principal, Capt. Gladstone Solomon; Dhurandhar retires
shortly thereafter.
1933
Receives a commission from the Maharaja of Chhota Udepur to do a
series of paintings; goes on to do commissioned work for other royal
families such as those of Aundh and Baroda.
1937
Travels to Europe on his maiden trip.
1942


Compiles his paintings and sketches of his two wives—in all one
hundred and seventy-five—and binds the collection, My Wife in Art,
with a preface written by himself.
1943
Starts sketching for the book, The Peoples of Bombay, being produced
by his old acquaintance Percival Strip and his sister Olivia Strip.
1944
Illustrates Fitzgerald’s version of The Rubaiyat of Omar Khayyam, published in Bombay by Thacker & Co. Ltd.
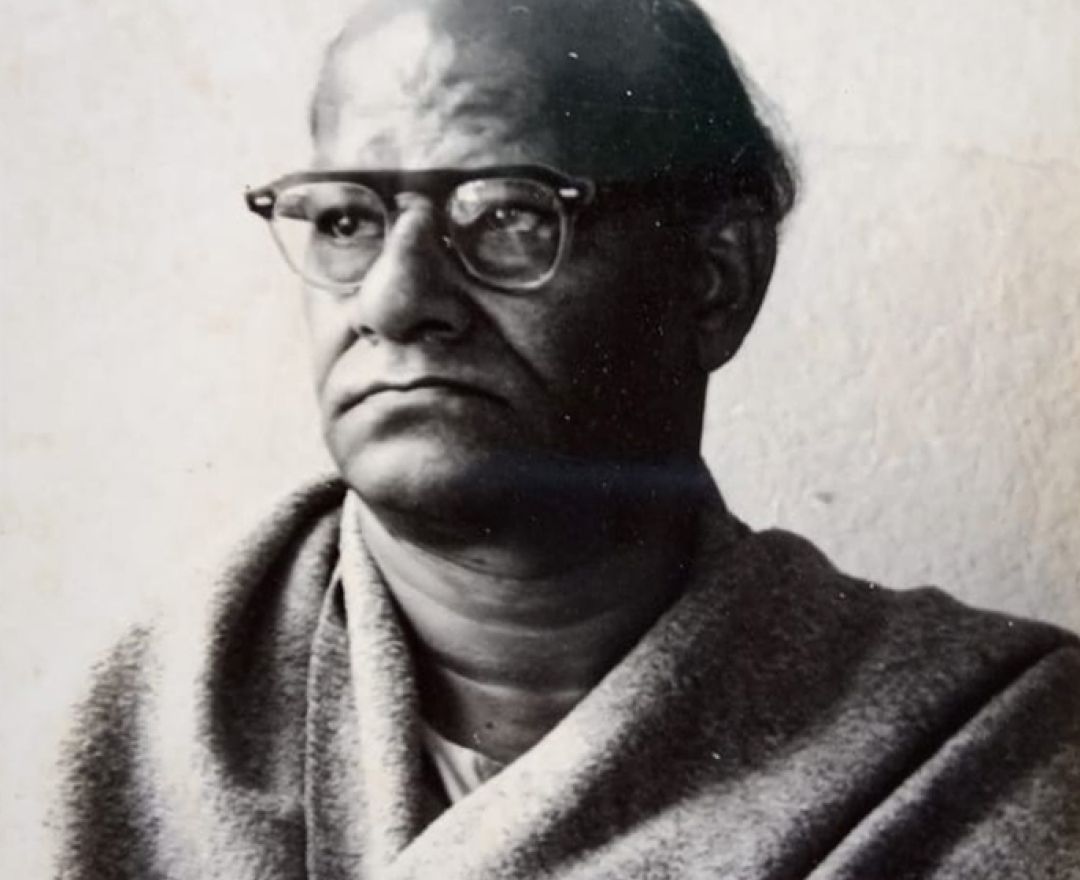
Falls ill in May, is bedridden for days; passes away on June 1 in
Bombay.
2018

National Gallery of Modern Art, Mumbai, supported by DAG,
holds a retrospective of the artist, titled 'M. V. Dhurandhar: The
Romantic Realist'. Curated by Suhas Bahulkar, chairman, advisory
committee, NGMA, Mumbai, the exhibition runs from September
11 to October 13.
2021
My Wife in Art is part of DAG’s exhibition, ‘Home is a Place:
Interiority in Indian Art’, at its gallery in New Delhi.