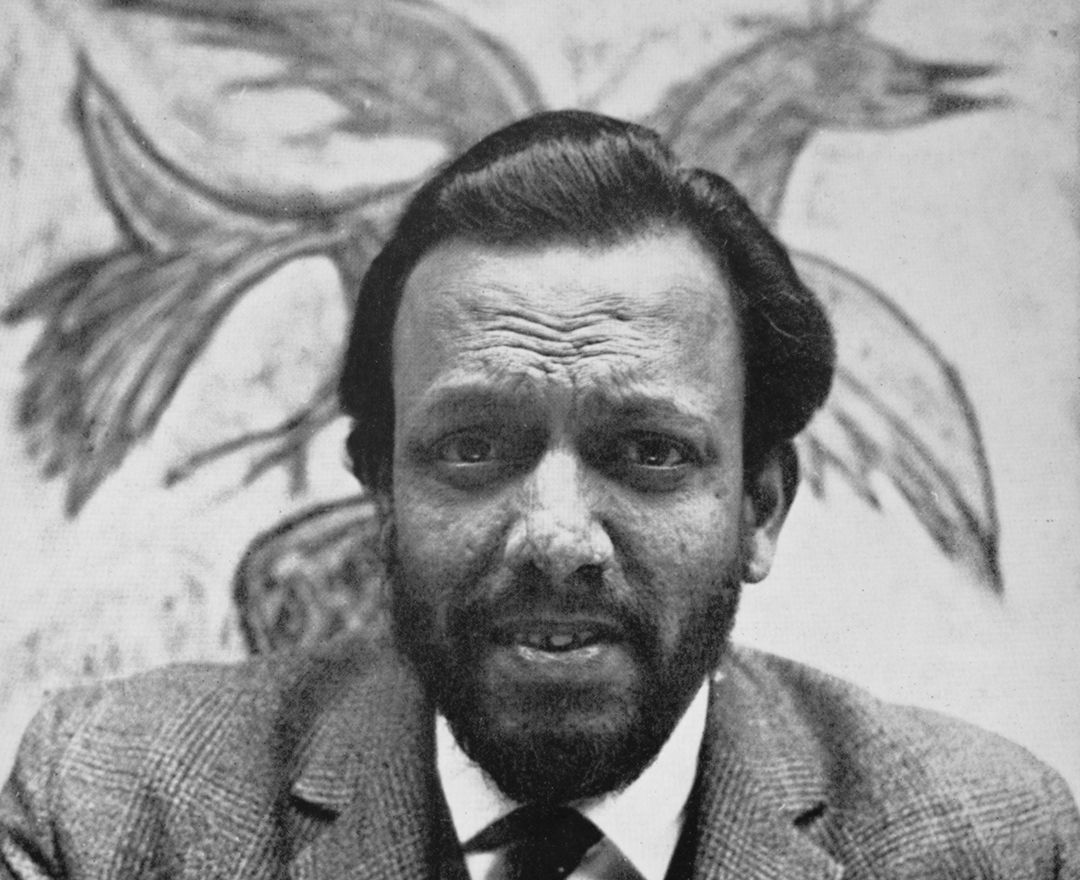
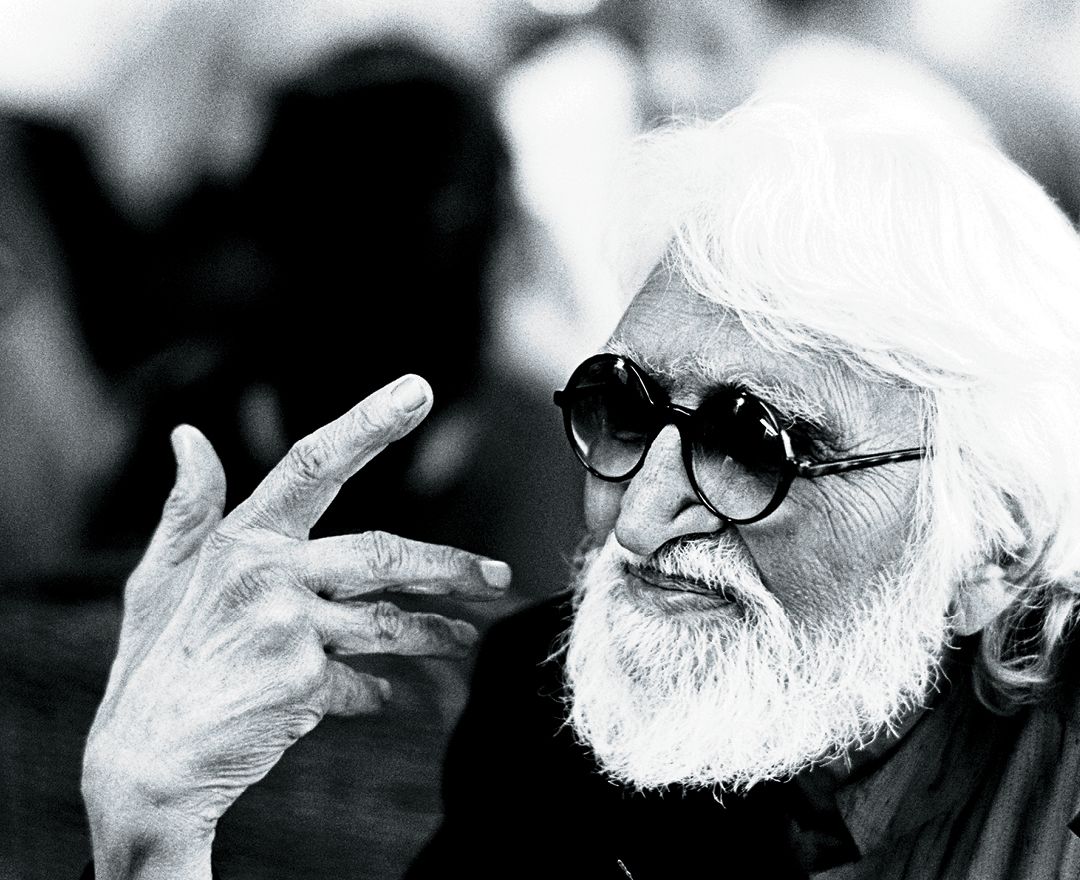
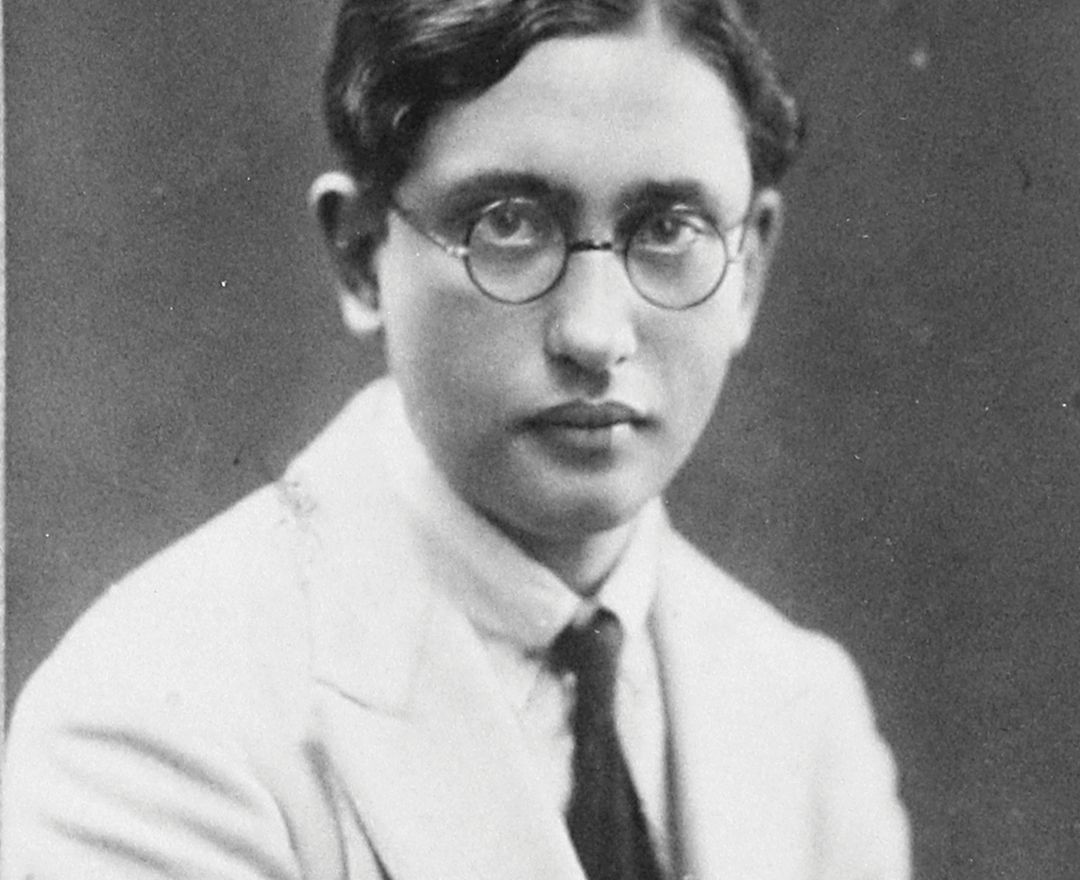
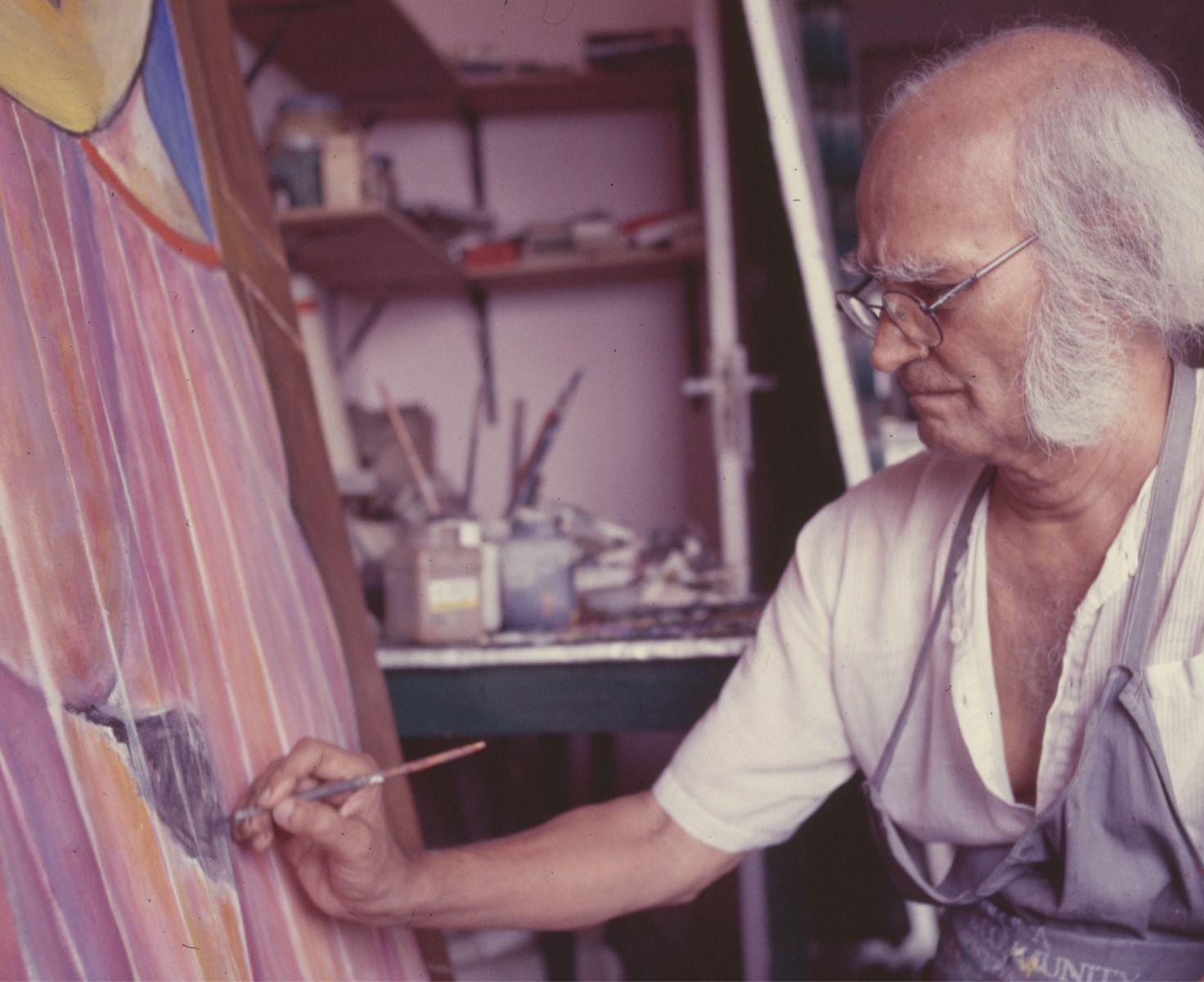
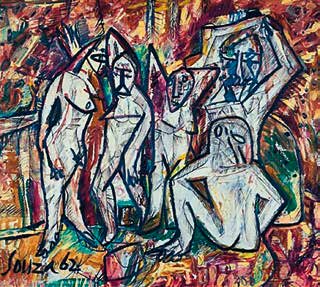F. N. SOUZA
FRANCIS NEWTON SOUZA ARTIST TIMELINE
ARTWORKS dag exhibitions notable collections
|
1924 - 2002 F. N. Souza |
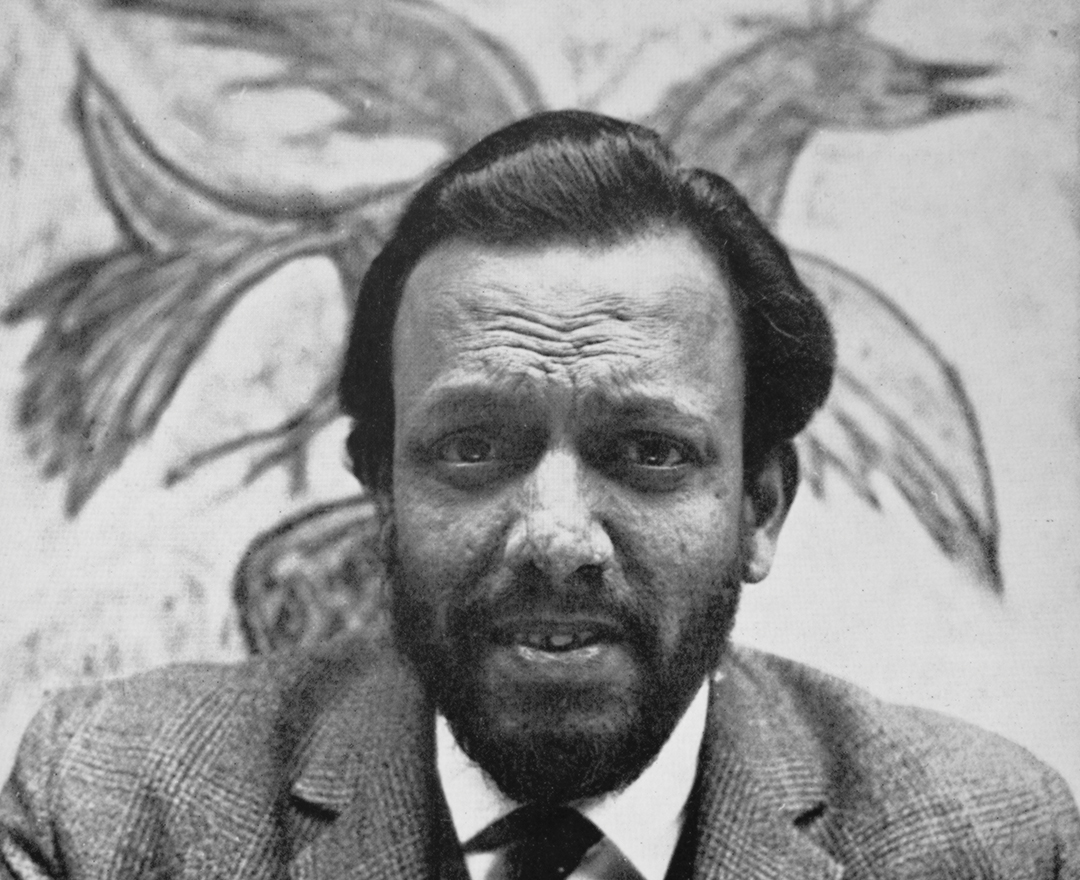
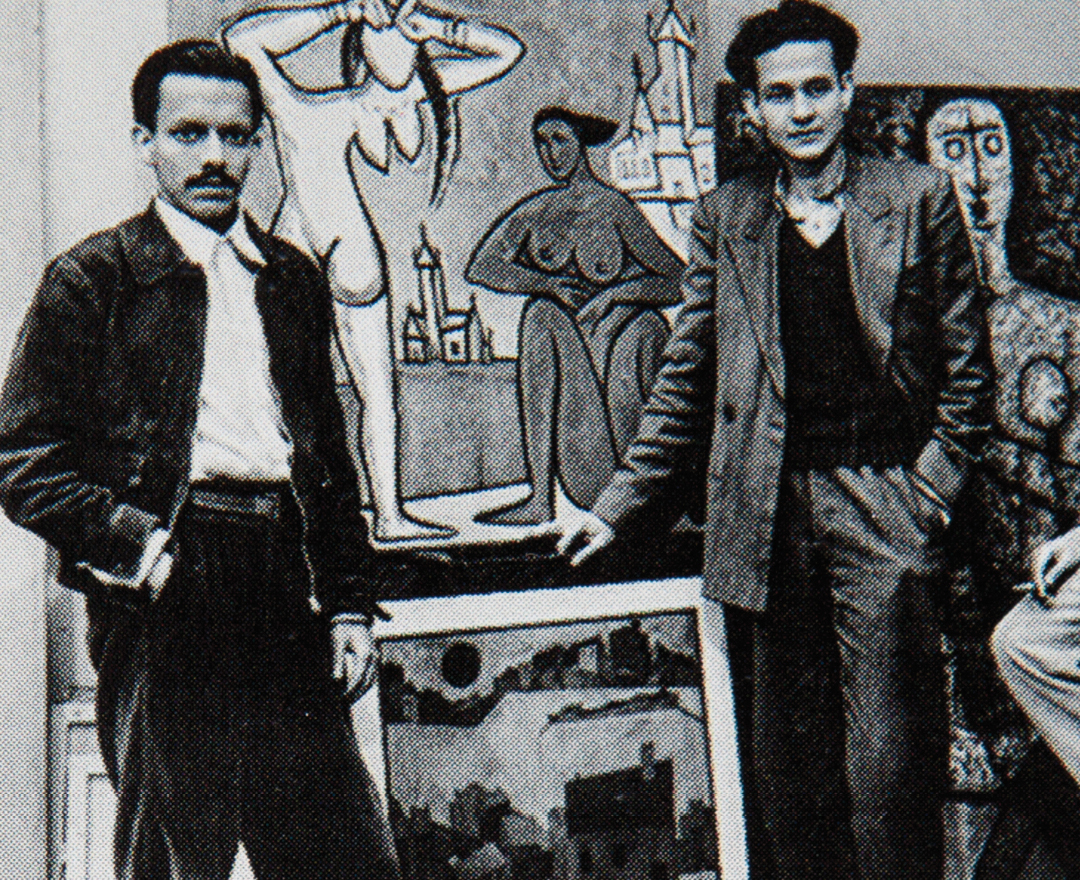
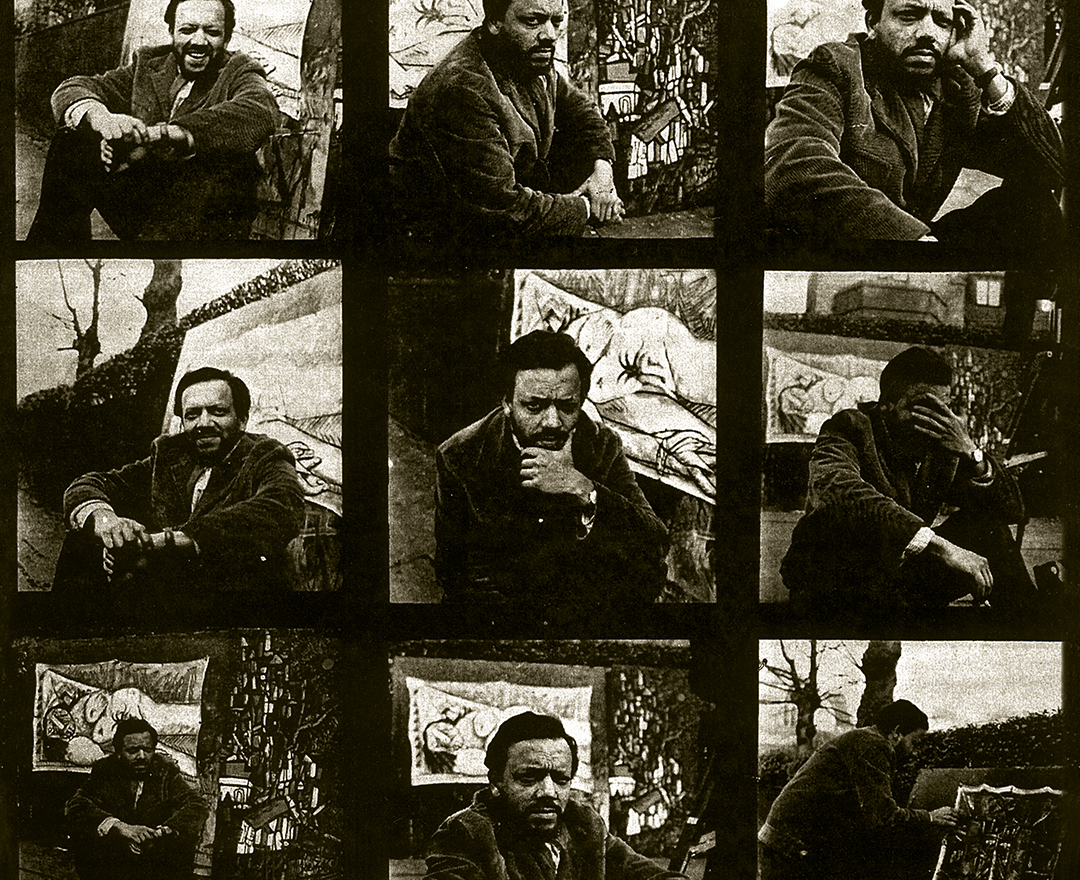
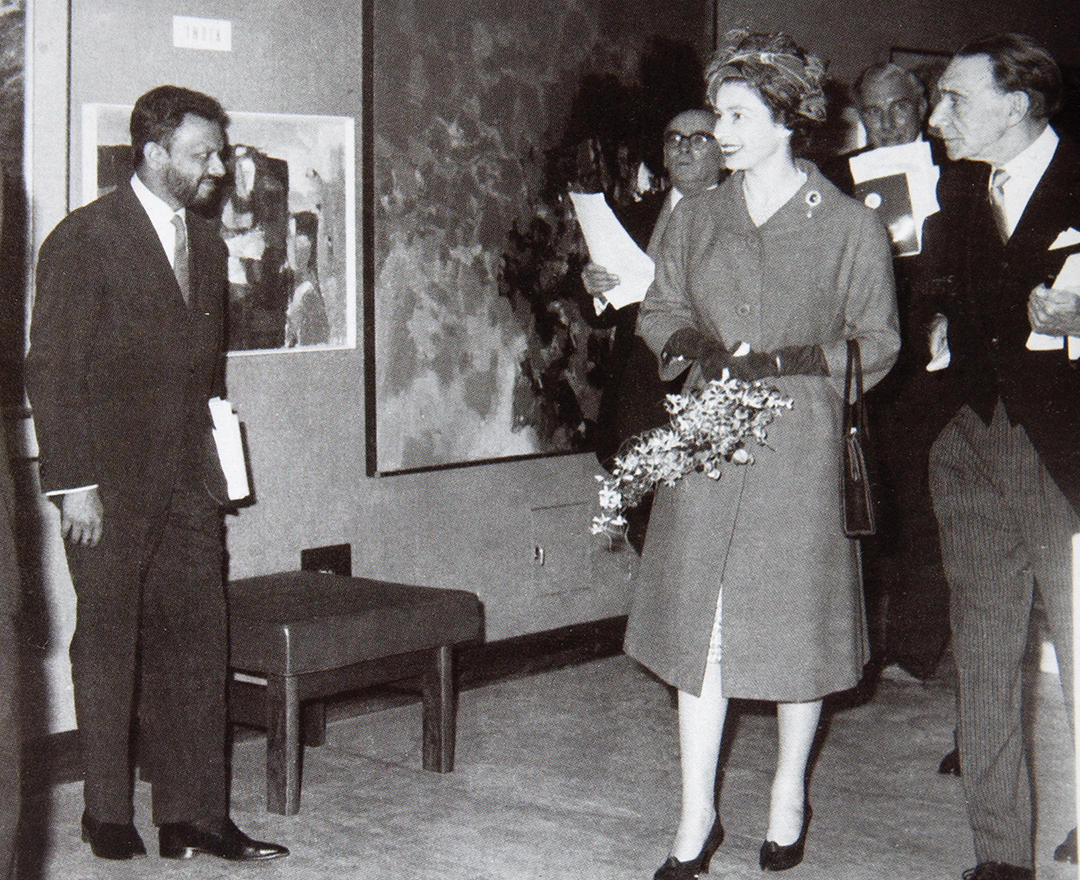
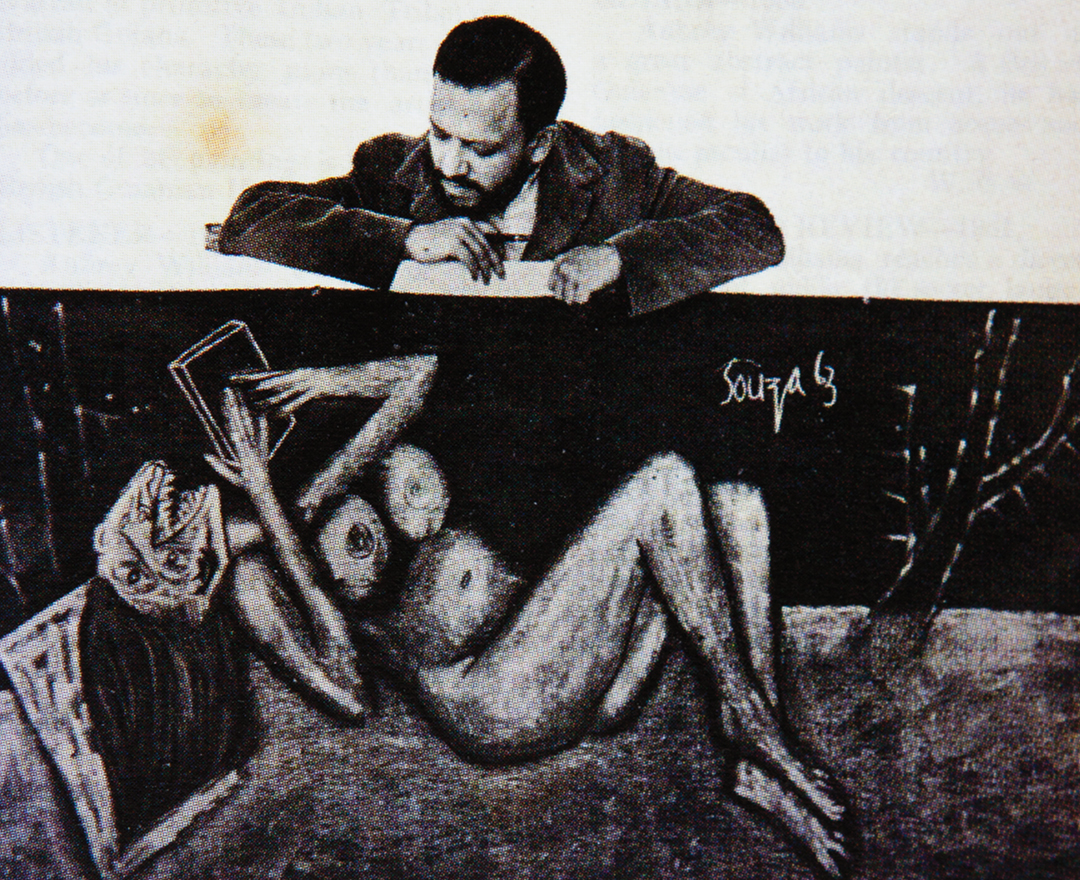
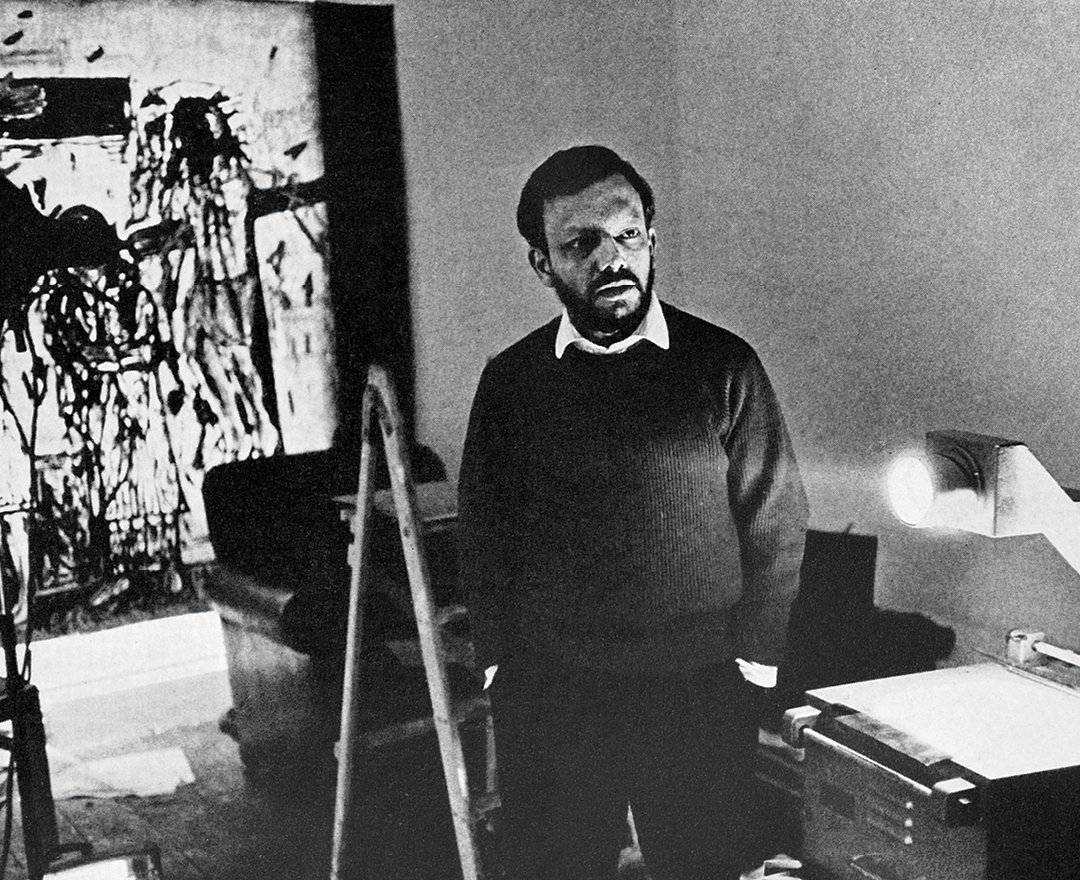
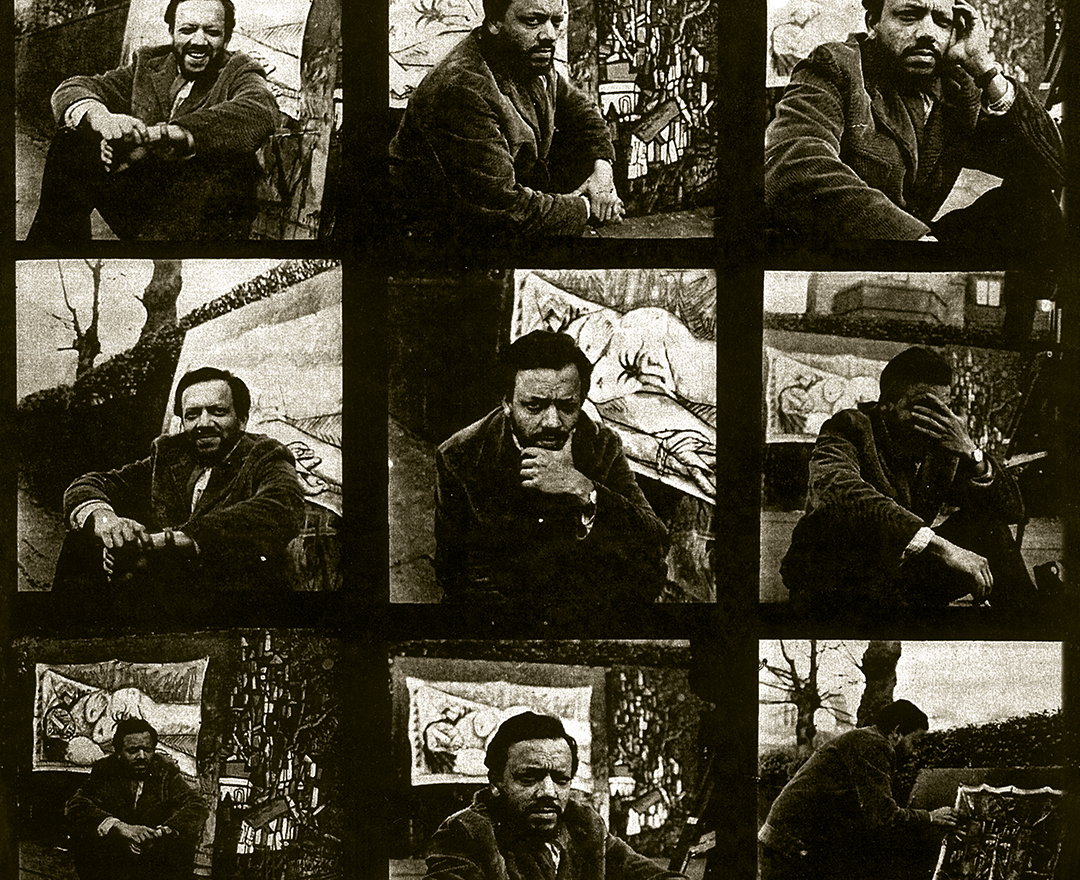







'We were bold and full of fire. We were forging a modern Indian art with a blast!'
F. N. SOUZA
artist timeline
artworks
dag exhibitions
|
‘Continuum: Progressive Artists’ Group’ |
|
DAG, New Delhi, 2011 |
|
The ‘Manifestations’ series of 20th Century Indian Art, Editions V, VI, VII, VIII, IX, X, XI |
|
DAG, New Delhi and Mumbai, 2011-14 |
|
‘The Printed Picture: Four Centuries of Indian Printmaking’ |
|
DAG, New Delhi, 2012; Mumbai, 2016; alternate locations in Kolkata, 2013; Jaipur, 2017; Chandigarh, 2018 |
|
‘Indian Landscapes: The Changing Horizon’ |
|
DAG, New Delhi, 2012 |
|
‘The Naked and The Nude: The Body in Indian Modern Art’ |
|
DAG, New Delhi, 2013; Mumbai, 2015 |
|
‘Mumbai Modern: Progressive Artists’ Group 1947-2013’ |
|
DAG, Mumbai, 2013 |
|
‘Indian Divine: Gods & Goddesses in 19th and 20th Century Modern Art’ |
|
DAG, New Delhi and Mumbai, 2014 |
|
‘Indian Abstracts: An Absence of Form’ |
|
DAG, New Delhi, 2014; Mumbai and New York, 2015 |
|
‘Indian Portraits: The Face of a People’ |
|
DAG, New Delhi, 2013; Mumbai, 2014 |
|
‘India Modern: Narratives from 20th Century Indian Art’ |
|
DAG, New York, New Delhi, Mumbai, 2015; Chandigarh, 2017 |
|
‘Memory & Identity: Indian Artists Abroad’ |
|
DAG, New York and New Delhi, 2016; Mumbai, 2017 |
|
Primitivism and Modern Indian Art’ |
|
DAG, Mumbai, 2019; New York, 2020 |
|
‘Navrasa: The Nine Emotions of Art’ |
|
DAG, Mumbai and New Delhi, 2020 |
|
‘The Fifties Show’ |
|
DAG, New Delhi, 2020 |
|
‘The Sixties Show’ |
|
DAG, New Delhi, 2019; Mumbai, 2020 |
|
‘Ways of Seeing: Women Artists | Women as Muse’ |
|
DAG, New Delhi, 2021 |
|
‘Indian Blue: From Realism to Abstraction' |
|
DAG, New Delhi, 2021 |
|
‘Iconic Masterpieces of Indian Modern Art’ |
|
DAG, Mumbai, 2021 |
notable collections
|
Kiran Nadar Museum of Art, New Delhi, India |
|
National Gallery of Modern Art, New Delhi, India |
|
Jehangir Nicholson Art Foundation, Mumbai |
|
Tata Institute of Fundamental Research Art Collection, Mumbai |
|
Piramal Art Foundation, Mumbai |
|
Government Museum and Art Gallery, Chandigarh |
|
CITI India Corporate Collection |
|
Haifa Museum, Haifa |
|
Glenbarra Art Museum, Himeji |
|
Tate Modern, London |
|
British Museum, London |
|
Victoria and Albert Museum, London |
|
The Hepworth Wakefield Art Gallery, Wakefield |
|
Museum of Biblical Art (Dallas), Texas |
|
Jane and Kito de Boer Collection, Dubai and London |